While the natural product industry spends most of its efforts on the beauty aspects of skincare, the market for skin conditions also offers a huge opportunity. Skin conditions affect almost 900 million people worldwide at any given time.[i] In the U.S., five skin conditions make up 80 percent of all skin diseases (acne, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, rosacea, skin cancer).[ii] The entire skincare market is enormous. The market size was valued at 104+ billion (USD) in 2022 and is projected to reach a valuation of USD 109.71 billion in 2023.[iii]
For centuries, people have been approaching skin health with topical applications, yet physiologically speaking, the best approach is “beauty from within.” Why? Skin cells grow from the inside out, not the outside in. We are now learning that consuming key nutrients will significantly impact skin health far beyond beauty.
Skin 101
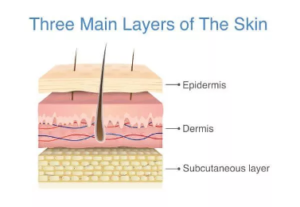
The skin is the body’s largest organ, yet it is often misunderstood. The skin’s structure comprises an intricate network that serves as the body’s initial barrier against pathogens, UV light, chemicals, and mechanical injury. It also regulates temperature and the amount of water released into the environment. The skin contains three layers: Epidermis, Dermis, and Subcutaneous. Each layer comprises different cells, which all possess different components and responsibilities.
Epidermis
The epidermis has two cell types: basal and squamous. Basal cells produce new cells and impact melanin and tactile cells, while squamous cells produce keratin (which is protective) and Langerhans (immune).
Dermis
The dermis comprises collagen, elastin, blood vessels, lymph vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, collagen bundles, fibroblasts, nerves, and sebaceous glands.
- Collagen supports the epidermis and its durability.
- Elastin allows the skin to spring back into place and provides flexibility.
Subcutaneous
The subcutaneous layer provides three benefits: Protection, Insulation, and Fat Storage. It consists mostly of collagen and fat.
What Harms Impacts Skin Health
For those familiar with my webinars, I often discuss those things that are “beneath the surface” (no pun intended with our topic of skin). Beneath the surface implies those physiological or biochemical “causes” of a health challenge. The following are contributing factors to poor skin health:
- Lack of Sleep
- Stress
- Hormone Imbalances
- Nutrient Depletions
- Allergies
- Diet
- Pollution
- Dehydration
- Sun/UV Light
- Other health conditions
- Bowel disorders
- Diabetes
- Microorganisms
- Weak Immune System
- Thyroid Problems
From the list above, many things can go wrong and contribute to skin health concerns. Let’s look at the common areas and some supplements we can utilize to help mitigate poor skin health issues.
Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress, or free radical damage, is difficult to avoid, either due to our body’s natural production or environmental exposure. Oxidative stress triggers the production of three enzymes that contribute to elastin degradation, hyaluronic acid, and collagen: Elastase, Hyaluronidase, and MMP (Metalloproteases). It will also provoke skin lipid peroxidation and various DNA damage.
Addressing Skin Oxidative Stress Naturally
There are numerous powerful antioxidant ingredients to help with neutralizing oxidative stress and have clinical proof they support skin health:
- Astaxanthin (ex. AstaPure®, AstaReal®)
- Indian gooseberry a.k.a. amla
- Red Orange ComplexTM
- Turmeric/Curcumin (HydroCurc®
Nutritional Support
This one may be too simple to mention, but it needs to be. We need to “feed the skin” key nutrients to help promote the proper production of essential cells. Here is a quick summary of the nutrients I would consider adding to my everyday diet or as a dietary supplement (functional food or beverage):
- Essential Fatty Acids
- Flavonoids: The list from Oxidative Stress (above) is a good start
- Minerals: Primarily Zinc and Selenium
- All essential minerals
- Peptides: Multiple Sources
- Vitamins: A, C, D, and E
Hydration
Inadequate hydration leads to many visible issues with your skin. These include:
- Dull Skin
- Wrinkles
- Lines
- Decreased Elasticity
- Cracks
- Blemishes
- Pore Visibility
Luckily, many nutritional supplements have proven health benefits for skin hydration.
Addressing Hydration Naturally
- Water
- Astaxanthin
- Collagen Peptides: Various
- HA Matrix: Dermial®
- Ceramides: Various
- Essential Fatty Acids
- Hyaluronic Acid
- Prebiotics: BeautyOLIGO®
- Probiotics: Various
Ceramides 101
Ceramides are relatively new to most people, so let’s briefly introduce their role in skin health. This is why ceramides are important:
- Ceramides are fats or lipids that are found in skin cells. They comprise 30% to 40% of your outer skin layer or epidermis.
- Their integrity is critical in maintaining skin permeability and guaranteeing optimal hydration.
- They are important for retaining your skin’s moisture, preventing the entry of germs into your body, protecting against UV damage, Reduce fine lines and wrinkles.
Note: There are numerous branded ingredients supporting ceramides.
Collagen and Skin Health
Collagen is the most abundant protein found in the body. Three types of collagens are found in the body (Type I, Type II, and Type III).
- Type I collagen is primarily found in the skin, tendons, and bones.
- Type II collagen is primarily found in cartilage.
- Type III collagen is primarily found in the skin, blood vessel walls, and the reticular fibers of most tissues.
We can see that the primary focus for skin health should be on both Types I and III.
Collagen and skin health can confuse the consumer and the natural product industry. I recently participated in the Collagen Symposium in Barcelona, where we broke down the differences in collagen products/ingredients available in the marketplace. For those who wish to learn more about collagen from experts in the field, please check out the link above; it will be worth your time. Moving on to our topic of skin health, two types of collagen ingredients are available for skin health: hydrolyzed collagen and HA Matrix (Dermial®). Let’s take a quick look at the differences.
Hydrolyzed Collagen
Hydrolyzed collagen refers to collagen broken down from its large protein molecule into the components that make up protein, i.e., amino acids and peptides. Breaking collagen down into these smaller pieces allows for better absorption. Skin health collagen products contain either hydrolyzed Type I, hydrolyzed type III, or a combination of both. The dosing required to achieve the benefits for skin requires much larger amounts than the HA Matrix, i.e., grams vs. milligrams. There are several branded hydrolyzed collagen products available in the market, with science showing benefits for skin health, elasticity, hydration, and more.
HA Matrix (Dermial®)[iv] [v]
Dermial® is a patented natural ingredient containing three key naturally occurring compounds, all of which benefit skin health: Hyaluronic Acid (HA), Collagen, and Polysaccharides.
Hyaluronic Acid
Hyaluronic acid is primarily found in the fluid of the eyes, joints, and skin. Its main function is to help the body retain water in tissue, i.e., Lubrication and Moisture. Its impact on the skin is to improve wound healing, decrease fine lines and wrinkles, decrease dry skin, reduce skin roughness, improve hydration, and improve elasticity.
Collagen
We mentioned the importance of collagen previously.
Sulfated polysaccharides (Dermatan and Chondroitin Sulfate)
Dermatan sulfate (DS) roles have been demonstrated in tissue development under the epidermis, blood vessels, and bone via an interaction with collagen. DS is essential for tissue development and the assembly of collagen fibrils in the skin.[vi] Chondroitin sulfate (CS) is a major component of the extracellular matrix (ECM) of many connective tissues, including cartilage, bone, skin, ligaments, and tendons. CS induces the expression of type I collagen and has the potential to facilitate skin regeneration, implying that CS could be clinically applied to improve skin aging.[vii]
Scientific data shows that Dermial®:
- Improves the hydration and elasticity of the skin.
- Acts as a potent regenerative agent
- Boosts the quality of the dermis and epidermis layers to help maintain skin health.
- Significantly increases the production of elastin.
- Increases the production of Type I collagen (Responsible for skin elasticity, firmness, and structure.).
- Promotes the production of Type III collagen (Supports the tensile strength of the skin).
- Increases the production of HA (in dermal fibroblasts).
Why not combine both hydrolyzed collagen with HA Matrix?
Combining a hydrolyzed collagen product with skin health efficacy with Dermial® is brilliant. Since one provides the nutritional components (amino acids and peptides) and the other helps support the body’s production of the compounds needed for skin health, it seems like a no-brainer to consume both.
Gut-Skin axis
The tie between gut health and the skin is not a difficult one. Modern medicine has shown that poor gut health is linked to atopic dermatitis, rosacea, psoriasis, and acne. Pathogenic bacteria and metabolites are linked to poor skin immunity and inflammatory reactions. An imbalance of good and bad bacteria contributes to:
- Altered Immune Response
- Nutrient Depletions
- Toxins
- Hormone Imbalances
Leading to:
- Skin Diseases
- Signs of Aging
- Redness
- Skin Sensitivities
Natural Solutions
- Prebiotic Fibers: Various
- Probiotics: Various
- Postbiotics: Various
- Synbiotics: Need more scientific evidence, but it looks promising.
We can see clearly that skin health and the fight to protect or repair from environmental and the effects of aging will take a multifaceted approach to be successful. My suggestion for those who desire to address their skin health aggressively is to incorporate at least one of the ingredients mentioned in each category above. Sometimes, you can address two or more areas with one ingredient. Learn more about your health and skin health supplements and then “jump in with both feet”!
References:
[i] Hay RJ, Johns NE, Williams HC, Bolliger IW, Dellavalle RP, Margolis DJ, Marks R et al. The global burden of skin disease in 2010: an analysis of the prevalence and impact of skin conditions. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:1527–34. doi:10.1038/jid.2013.446
[ii] Amrican Academy of Dermatology Association website, https://www.aad.org/media/stats-numbers#:~:text=Acne%20is%20the%20most%20common,to%2050%20million%20Americans%20annually.&text=Acne%20usually%20begins%20in%20puberty,experience%20at%20least%20minor%20acne., “Skin Conditions by the Numbers, Accessed June 21, 2023
[iii] Fortune Business Insights website, Skincare Market Size, Share & COVID-19 Impact Analysis, By Product (Creams, Lotions, Powders, Sprays, and Others), Packaging Type (Tube, Bottle, Jar, and Others), Gender (Men and Women), Distribution Channel (Cosmetic Stores, Supermarkets/ Hypermarkets, Online Channels, and Others), and Regional Forecasts, 2023-2030, https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/skin-care-market-102544, published June 2023, accessed June 23, 2023
[iv] Torrent, A et al. The FASEB Journal, 2013;1S:633.2.
[v] Gálvez et al. Experimental Biology 2022 Meeting Abstracts
[vi] Mizumoto S, Yamada S. The Specific Role of Dermatan Sulfate as an Instructive Glycosaminoglycan in Tissue Development. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 5;23(13):7485. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137485. PMID: 35806490; PMCID: PMC9267682.
[vii] Min D, Park S, Kim H, Lee SH, Ahn Y, Jung W, Kim HJ, Cho YW. Potential anti-ageing effect of chondroitin sulphate through skin regeneration. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2020 Oct;42(5):520-527. doi: 10.1111/ics.12645. Epub 2020 Aug 20. PMID: 32583476.